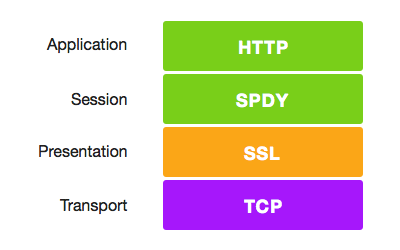
An early bird’s eye of let’s make the web faster initiative – SPDY (pronounced as “SPeeDY”) came into existence with the goal to mark a substantial decrement in Website Load time. It didn’t imprint the replacement of HTTP but modularised it with the HTTP 1.1 by enumerating no. of features to nimble up web transactions.

SPDY was evolved by Google and soon prospered on almost all the Google Products.In a short span of time, big Tech companies like Facebook, Twitter and WordPress.com soon practiced it.
This article will feature on the basics of SPDY and its functionalities in accelerating your Web Performance.
SPDY Design and features
SPDY adapts itself into the existing architecture by adding a session layer onto an SSL that allows for multiple concurrents, interleaved streams over a Single TCP Connection.
Supported platforms
- CentOS/Fedora (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Debian/Ubuntu (32-bit and 64-bit)
System Requirements
- Apache 2.2 (≥2.2.4)
- mod_ssl enabled
Before encroaching into the features of SPDY let’s dive deep into the problems that SPDY solves.
Problems that popularised in HTTP 1.1
With HTTP 1.1 number of bugs creeped in affecting the request and response between a client and server. These flaws aggregated to website performance.
Note: Check your website performance, try these online free tools:
webpagetest.org and gtmetrix.com
SPDY is incorporated with the objective of providing functionality that aids in resolving following:
Scarce number of connections
The approach through which HTTP is designed, it says that each resource crave for a separate HTTP request to a server. On an average modern browser supports up to 6 concurrent connections with server. This shows if more than stated connections are required from the same server the browser will have to wait until one among the allocated resources has been downloaded before it can open another request. this phenomenon has significant effect on the page load time.
With the advent of HTTP pipelining this problem was about to elope but it is still penalised with First-In, First-Out (FIFO) problem.
Note: Research accomplished by HTTPArchive shows that the average web page consists of 84 requests from 30 different domains.
HTTP HEADERS
The second issue in HTTP bucket is the use of uncompressed and unnecessary headers.
HTTP headers serves as fundamental to web transactions work but all this has to be directed through wire and so more header you have, the longer request will take.
Today’s technologies that compress the headers are usually optional. There exists still, the potential for compressing or emitting headers that are not required.
Developer workarounds
Web developers have strategically adopted numerous techniques to decrease load times. Few among them are:
- Image Sprinting– Combining number of smaller images into one image ‘sprite’ and then using CSS to display the correct section of the sprite on the required page.
- Concatenation and minification– Combining multiple CSS or Js files in order to reduce the HTTP requests for a page. Whilst minification corresponds to the art of removing whitespace and other supplementary content within the files to reduce their size.
- Domain Sharding– Putting the resource under sub-domains so that the browser can open more parallel connections.
- Inline Resources– Using the Data URIs to embed the HTML code resulting in decreasing the number of HTTP requests.
Since all these strategies are useful in escalating the load time still, they are very cumbersome to implement.
Troubleshooting these with SPDY
Let us take a look of some of the features that SPDY aims to fix
Multiplexed streams
SPDY accounts for unlimited concurrent streams over a single TCP Connection. Since the requests are interleaved on a single channel the efficiency turns out to be much higher in terms of fewer network connection, fewer but more densely packed , packets are issued.
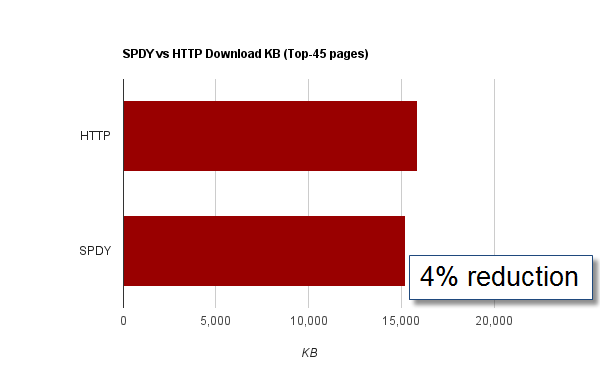
Reducing Download Bytes
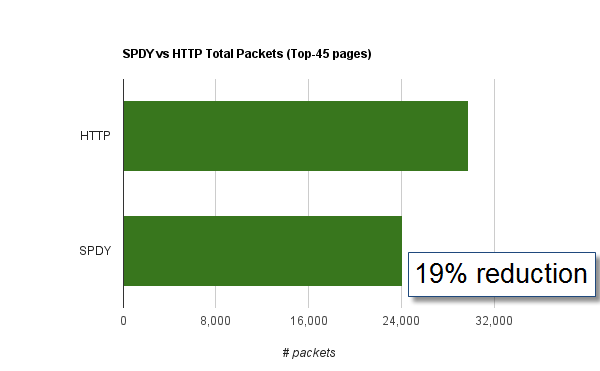
Reducing Total Packets
Request Prioritization
SPDY flow include prioritization. Server can be instructed to send the important resources as soon as the available bandwidth is ensured. This helped to overcome First-in First-out problem.
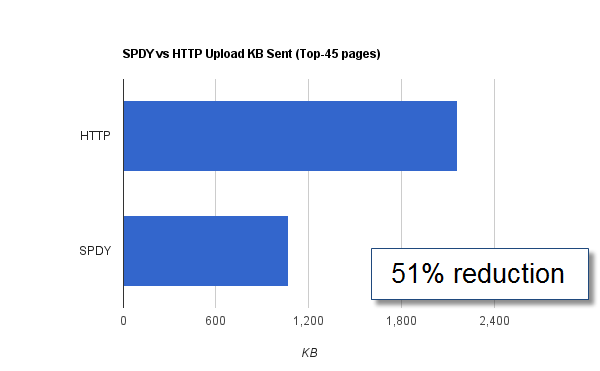
HTTP Header compression
SPDY compresses the request and response HTTP Headers, resulting in fewer packets in transmission with fewer bytes.
Server Push
This a salient feature of SPDY and has an ability to create server-initiated streams. This allow server to push resources down to client prior to client’s request for the same.
This is in command with Data URIs to embed images within the same HTML markup page as We know the required resources to be requested thus eliminating the need for extra request.
Using SPDY Today
Now since you are well versed in SPDY basics and functionalities you can put this into use and reap benefits. The primary gain from SPDY is readily availability primetime. The major notable point is that SPDY requires SSL. This generates a slight latency penalty but ensures a secure connection between the communicating nodes.
Browsers that back up SPDY – Chrome, Opera, and Mozilla Firefox. Microsoft is also among the peers.
Check if a website properly supports the SPDY protocol, the super fast HTTP replacement and troubleshoot any problems with the configuration.- SPDYCheck.org
Disadvantage of SPDY protocol is cPanel doesn’t yet support HSTS and SPDY seamless integration for https only websites. Also some browsers doesn’t have any clue about this and serve the website on both http and https even if you have 301 redirects to one URL on https, this makes duplicated pages and get the website penalised by search engines.
We at IBEE Hosting have experts to configure your Dedicated Hosting Servers with SPDY and HSTS protocols to make your website speedy and at the same time avoid content duplication.